Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning: What’s the Difference? 8 key differences you will come to know
Introduction
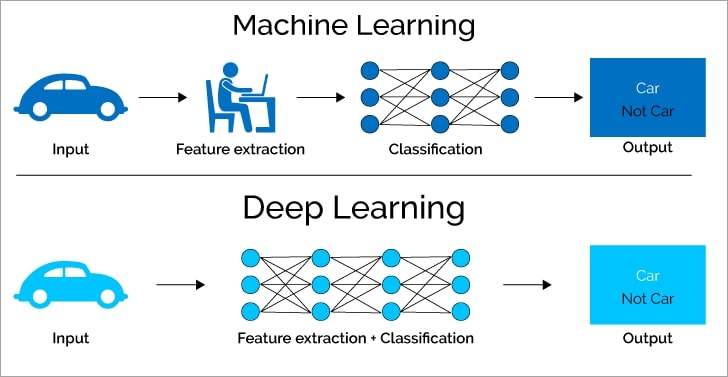
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve, two critical subfields—Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)—are at the forefront of innovation. While both are integral to AI development, they differ in complexity, applications, and functionality. Understanding Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning is essential for businesses, researchers, and AI enthusiasts aiming to leverage these technologies effectively.
In this article, we will explore the key differences, similarities, and applications of Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), providing a comprehensive view of their impact on various industries.
Table of Contents
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
Key Characteristics of Machine Learning
- Works primarily with structured data.
- Requires feature engineering, meaning manual selection of important data points.
- Effective for predictive analytics and pattern recognition.
- Can be categorized into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
Examples of Machine Learning Applications
- Email Spam Filtering: ML models classify emails as spam or not spam.
- Fraud Detection: ML is used to identify fraudulent transactions in the Banks.
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and YouTube suggest content based on user behavior.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning (DL) is a specialized subset of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks to simulate human brain processes. Unlike ML, deep learning can handle large amounts of unstructured data without extensive manual input.
Key Characteristics of Deep Learning
- Uses multi-layered neural networks (hence “deep”).
- Can process unstructured data such as images, text, audio, and video.
- Automatically learns important features without manual selection.
- Requires large datasets and substantial computational resources.
Examples of Deep Learning Applications
- Facial Recognition: Used in security systems and social media tagging.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on deep learning models.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Voice assistants like Alexa and Siri use DL to process and understand human speech.
Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning: Key Differences
| Feature | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirement | Works with small to medium datasets | Requires large datasets |
| Feature Engineering | Needs manual selection of features | Learns features automatically |
| Complexity | Less complex | Highly complex |
| Computational Power | Works on regular computers | Requires GPUs and powerful hardware |
| Training Time | Faster training | Requires longer training time |
| Interpretability | More interpretable | Often considered a “black box” |
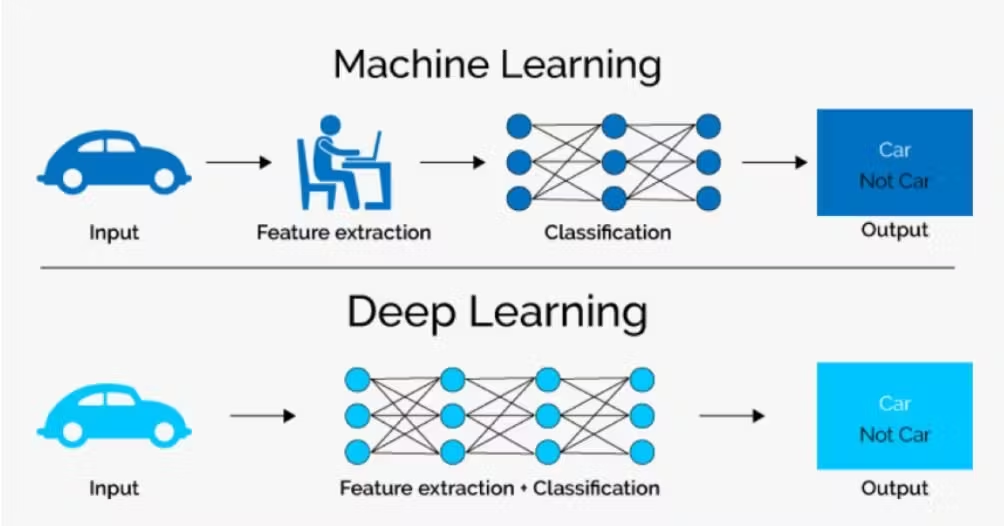
How Do Machine Learning and Deep Learning Work?
How Machine Learning Works
- Data Collection: Gather structured data for training.
- Feature Selection: Identify key variables manually.
- Model Training: Train using algorithms like Decision Trees, Random Forest, or SVM.
- Evaluation & Prediction: Test the model and refine predictions.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Train model
model = RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluate
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'Model Accuracy: {accuracy*100:.2f}%')
How Deep Learning Works
- Data Collection: Gather large unstructured datasets.
- Neural Network Setup: Define layers of neurons.
- Feature Extraction: Model identifies patterns automatically.
- Backpropagation & Optimization: Adjusts network weights for accuracy.
- Prediction & Decision Making: Produces results from trained data.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
# Build a simple neural network
model = Sequential([
Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(X_train.shape[1],)),
Dense(32, activation='relu'),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train model
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)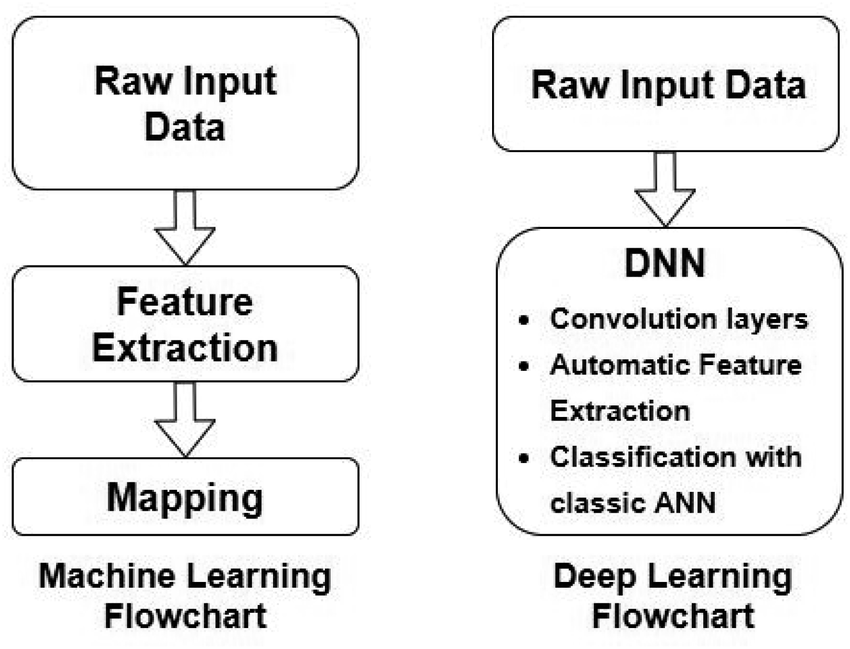
When to Use Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
Use Machine Learning When:
- You have small or medium datasets.
- You need a quick, interpretable solution.
- Working with structured data.
- Low computational power is available.
Example Use Cases:
Predictive maintenance, spam detection, customer segmentation.
Use Deep Learning When:
- Large amounts of data are available.
- Advanced AI models are required.
- Working with unstructured data (images, text, audio, video).
- Access to GPUs/TPUs for computation.
Example Use Cases:
Image/speech recognition, self-driving cars, medical imaging diagnostics.
Challenges in Machine Learning & Deep Learning
Machine Learning Challenges
- Feature engineering can be time-consuming.
- Difficulty with complex problems requiring deep insights.
- Performance heavily depends on data quality and preprocessing.
Deep Learning Challenges
- Requires large datasets for accuracy.
- High computational requirements (GPUs, TPUs, cloud services).
- Hard to interpret results (the “black box” problem).
Future of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine Learning and Deep Learning are continuously reshaping AI and automation. They are driving advances in intelligent decision-making, data analysis, and efficiency across industries.
Advancements in Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- Automated Machine Learning (AutoML): Simplifies model building for non-experts.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Enhances transparency and trust in AI models.
- Edge AI & On-Device Learning: Deploying ML/DL models directly on devices for real-time decisions.
- Reinforcement Learning Enhancements: Enables sophisticated adaptive AI in robotics, gaming, and autonomous systems.
- Neural Architecture Search (NAS): Automates deep learning model optimization.
Challenges in the Future of ML and DL
- Data Privacy & Security: Protecting sensitive data remains critical.
- Bias & Fairness in AI: Models must avoid amplifying biased outcomes.
- Energy Consumption: Large models require significant computational resources.
- Generalization & Transfer Learning: Improving adaptability to new tasks without retraining.
- Regulation & Ethical AI: Policies are needed to ensure safe, responsible AI dep
Machine learning and deep learning will continue to drive technological advancements, making AI more accessible, powerful, and efficient. Overcoming challenges related to ethics, privacy, and computational efficiency will be crucial in shaping a responsible and sustainable future for AI. As these technologies evolve, they will unlock new possibilities, revolutionizing industries and enhancing human-machine collaboration.
Upcoming Trends
More transparent and explainable deep learning models.
AI-powered robotics integrating ML & DL.
Edge AI enabling on-device ML/DL processing.
AI in healthcare enhancing diagnostics and drug discovery.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning is essential for selecting the right AI approach. ML works best with structured data, offering fast implementation and interpretability, while DL excels with large unstructured datasets, powering advanced AI applications like autonomous vehicles and image recognition.
At TechToGeek.com, we provide resources and insights to help you stay ahead in the evolving AI landscape. By leveraging ML and DL effectively, businesses and developers can unlock innovative solutions and drive progress across industries.
For more insights on AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning, stay tuned to TechToGeek! 🚀
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning?
Machine Learning relies on structured data and requires feature engineering, whereas Deep Learning uses neural networks to automatically learn features from large unstructured datasets.
2. Which one is better: Machine Learning or Deep Learning?
Neither is universally better; the choice depends on your data size, type, computational resources, and the complexity of the problem.
3. Do I need a GPU to use Deep Learning?
Yes, most deep learning models require GPUs or TPUs due to high computational demands.
4. Can Machine Learning handle unstructured data?
Machine Learning can handle limited unstructured data with preprocessing, but Deep Learning is better suited for raw unstructured data like images, audio, and text.
5. Where can I learn more about AI, ML, and DL?
For educational resources, tutorials, and insights, visit TechToGeek.com.