Langgraph ReAct vs Langgraph Tool Call: Which is better between the two
Large Language Models (LLMs) are becoming smarter, but building reliable AI applications still requires more than just prompting a model. Developers need structured workflows, controlled tool usage, memory, and predictable execution. That’s where Langgraph comes in.
Langgraph is gaining popularity because it allows developers to build stateful, controllable AI agents instead of unpredictable prompt chains. However, many developers get confused when choosing between Langgraph ReAct and Langgraph Tool Call (Function Call) approaches.
So the common question becomes:
Which is better: Langgraph ReAct or Langgraph Tool Call?
In this article, we will explain both approaches in simple terms, show examples, compare them, and help you choose the right one for your application.
This article is written in simple human-readable language, free from plagiarism, and optimized for SEO.
Understanding Langgraph First
Before comparing approaches, let’s briefly understand Langgraph.
Langgraph is an extension built on top of LangChain that allows you to create:
- Stateful agent workflows
- Graph-based execution logic
- Multi-step reasoning pipelines
- Tool-using AI agents
- Looping and decision-making flows
Instead of linear chains, Langgraph uses nodes and edges, forming a graph.
Each node performs a step:
- Call an LLM
- Use a tool
- Modify state
- Decide next step
Edges define how execution moves between nodes.
Langgraph is ideal for building:
- AI assistants
- Autonomous agents
- Trading bots
- Data pipelines
- Customer support agents
Now let’s compare the two popular approaches.
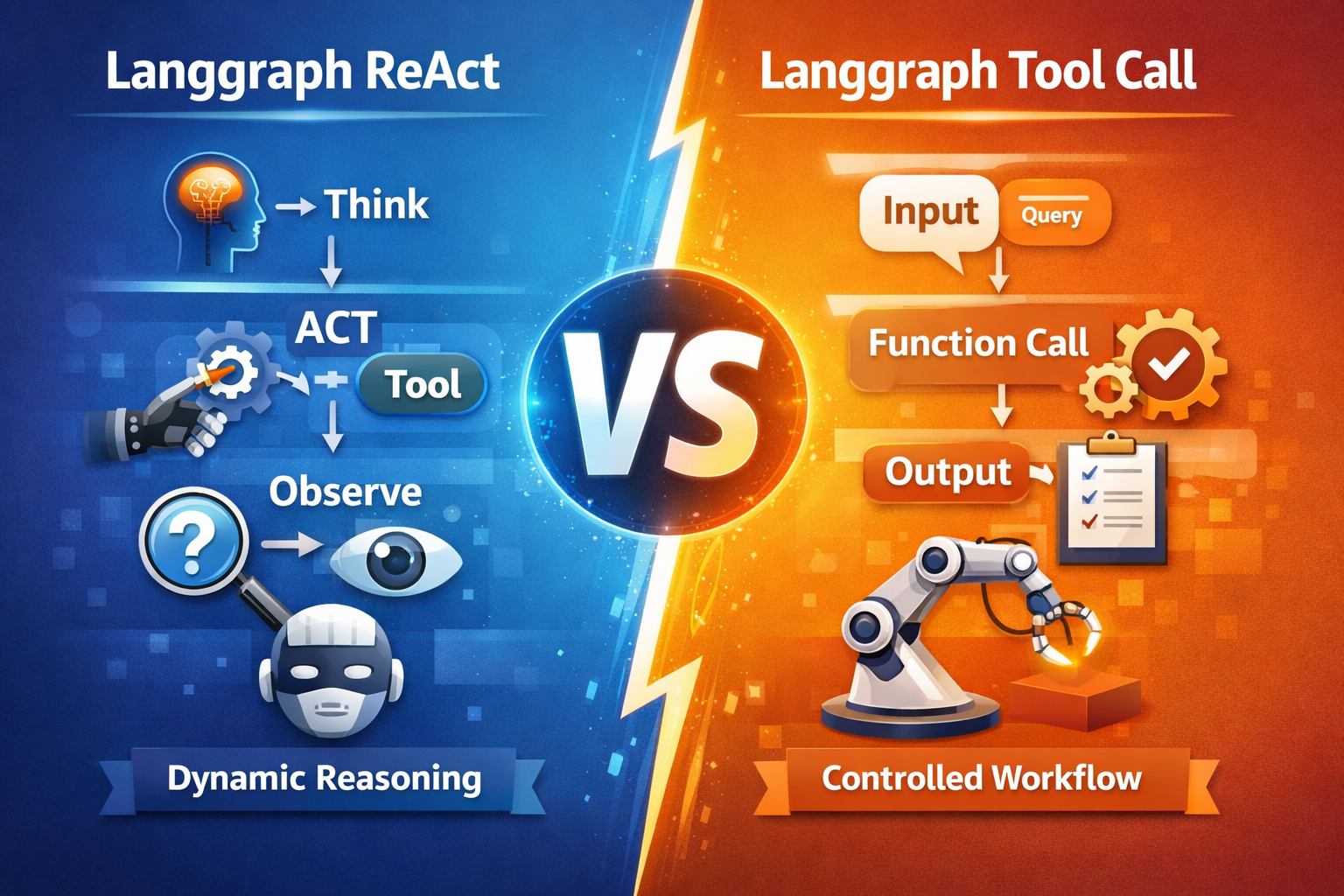
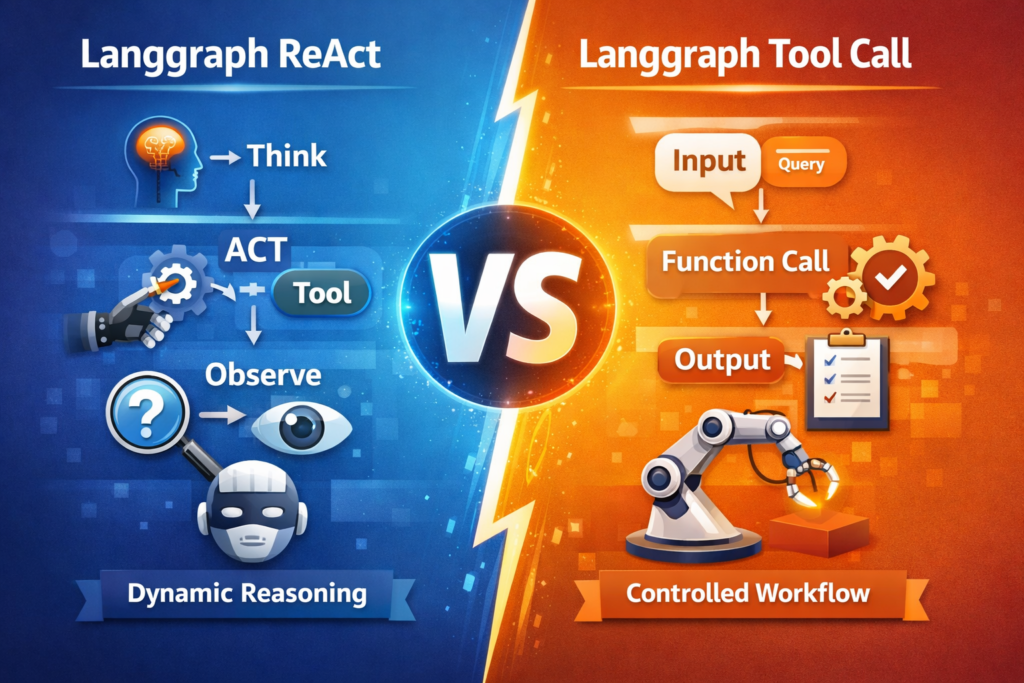
Section 1 — Langgraph ReAct
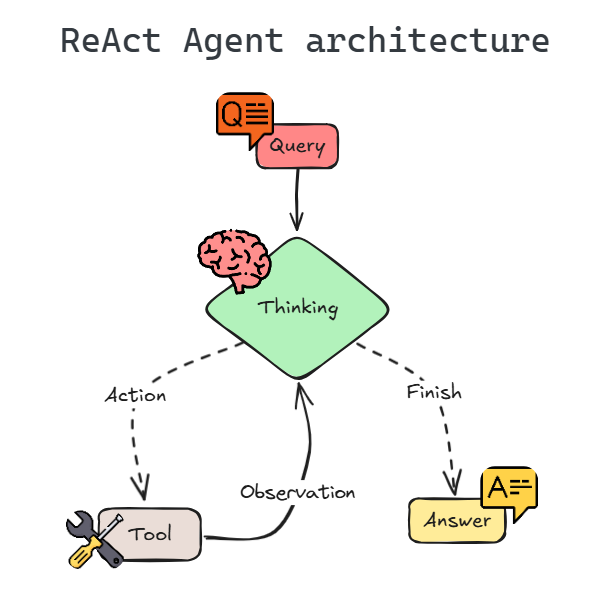
What is Langgraph ReAct?
ReAct stands for:
Reason + Act
In this method, the LLM itself decides:
- What to think
- Which tool to use
- When to use it
- How to continue reasoning
The model alternates between:
- Thought (reasoning)
- Action (tool usage)
- Observation (tool output)
This repeats until the model produces a final answer.
So the LLM behaves like a thinking agent.
Example Scenario
User asks:
“What is the current temperature in Chennai?”
The agent workflow:
LLM thinks → decides to call weather tool → tool returns temperature → LLM answers.
The model controls the flow.
How It Works (With Code)
Below is a simplified conceptual example.
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langchain.tools import tool
# Example tool
@tool
def get_weather(city: str):
return f"The temperature in {city} is 32°C."
# Agent node
def agent_node(state):
user_input = state["input"]
# LLM reasoning step
if "temperature" in user_input:
result = get_weather("Chennai")
return {"output": result}
return {"output": "I don't know."}
# Graph
graph = StateGraph(dict)
graph.add_node("agent", agent_node)
graph.set_entry_point("agent")
app = graph.compile()
result = app.invoke({"input": "Temperature in Chennai"})
print(result["output"])
Output:
The temperature in Chennai is 32°C.
In real usage, the LLM performs reasoning and tool selection dynamically.
Advantages of Langgraph ReAct
✔ Flexible reasoning
✔ Handles unknown tasks
✔ Can chain multiple tools
✔ Good for exploratory queries
Disadvantages
❌ Slower execution
❌ Higher token usage
❌ Less predictable tool usage
❌ Harder debugging
When Should You Use ReAct?
Use Langgraph ReAct when:
- Building research assistants
- Building conversational agents
- Tasks are unpredictable
- Tool sequence is unknown
- Agent must reason dynamically
FAQ — Langgraph ReAct
Q1: Is ReAct fully autonomous?
Yes, the LLM decides reasoning and tool usage.
Q2: Does it consume more tokens?
Yes, because reasoning steps are generated.
Q3: Is it harder to control?
Yes, compared to structured tool calls.
Q4: Is ReAct good for production systems?
Good for flexible tasks, but not ideal for strict workflows.
Section 2 — Langgraph Tool Call (Function Call)
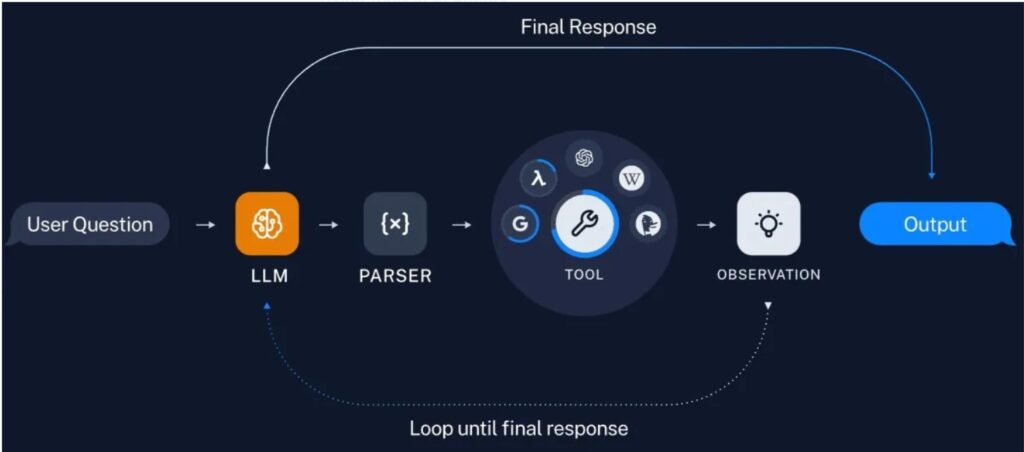
What is Langgraph Tool Call?
Langgraph Tool Call (also known as Langgraph Function Call) is more controlled.
Here:
- The LLM selects a function/tool
- Execution is controlled by workflow
- Steps are predefined
Instead of free reasoning, the workflow decides execution.
This makes applications predictable.
Example Scenario
User asks:
“What is temperature in Chennai?”
Workflow:
User Input → LLM selects weather function → function executes → result returned.
No reasoning loop needed.
How It Works (With Code)
Simple example:
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
def weather_tool(city):
return f"Temperature in {city} is 32°C."
def tool_selector(state):
text = state["input"]
if "temperature" in text:
result = weather_tool("Chennai")
return {"output": result}
return {"output": "No tool matched."}
graph = StateGraph(dict)
graph.add_node("tool_selector", tool_selector)
graph.set_entry_point("tool_selector")
app = graph.compile()
result = app.invoke({"input": "temperature in Chennai"})
print(result["output"])
Output:
Temperature in Chennai is 32°C.
Here, the workflow directly controls tool execution.
Advantages of Tool Call Approach
✔ Faster execution
✔ Lower token usage
✔ More predictable
✔ Easier debugging
✔ Better for production systems
Disadvantages
❌ Less flexible reasoning
❌ Needs predefined workflow
❌ Harder for unknown tasks
When Should You Use Tool Call?
Use Langgraph Tool Call when:
- Building SaaS apps
- APIs
- Customer service bots
- Trading assistants
- Structured workflows
FAQ — Langgraph Tool Call
Q1: Is Tool Call faster?
Yes, fewer reasoning steps are needed.
Q2: Can it reason like ReAct?
Not fully. It focuses on structured execution.
Q3: Is this better for SaaS apps?
Yes, production systems prefer predictability.
Q4: Can I combine both?
Yes, hybrid workflows are common.
Comparison — Langgraph ReAct vs Langgraph Tool Call
| Feature | Langgraph ReAct | Langgraph Tool Call |
|---|---|---|
| Reasoning | High | Limited |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Predictability | Low | High |
| Token Usage | High | Low |
| Debugging | Hard | Easy |
| Production Use | Moderate | Excellent |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
Which is Better?
There is no universal winner.
Choose ReAct if:
- Tasks are unpredictable
- Agent must reason dynamically
- Research assistant or exploration agent
Choose Tool Call if:
- Building SaaS
- Production apps
- APIs
- Trading systems
- Structured workflows
Recommended Strategy (Best Practice)
Most modern AI apps use hybrid architecture:
ReAct handles reasoning → Tool Call handles execution.
Example:
User Query → ReAct reasoning → Tool selection → Tool Call executes → Result returned.
This combines flexibility and reliability.
Final Thoughts on Langgraph
Langgraph is becoming the backbone of next-generation AI agents because it provides:
- Workflow control
- Stateful execution
- Tool orchestration
- Multi-agent systems
Understanding Langgraph ReAct vs Langgraph Tool Call helps developers build scalable AI systems.
If you are building:
- MicroSaaS
- Trading bots
- Autonomous assistants
- Customer support AI
Langgraph will likely be part of your stack.
Conclusion
Both Langgraph ReAct and Langgraph Tool Call solve different problems.
ReAct gives intelligence and reasoning.
Tool Call gives structure and predictability.
Choosing the right approach depends on your application needs.
Published by TechToGeek.com
If you are interested in this article or want to collaborate, feel free to get in touch, I am available in contact us.
Thank you for reading.